May 5, 2023
The US federal budget deficit for the calendar year 2022 was $1.42 trillion, down significantly from $3.35 trillion in 2021.

The US federal budget deficit as a percentage of GDP declined back to 5.4% in 2022, down from 11.9% in 2021 and 14.9% (which was the highest figure since World War II).

The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) projects that the US federal budget deficit as a percentage of GDP will decline to 5.3% in 2023, and then gradually rise to 6.9% in 2033. These projected deficits are significantly larger than the 3.6% of GDP that deficits have averaged over the past 50 years.

Over the past year, these estimated deficits have increased due to new legislation and poorer-than-expected economic performance.

The projected gradual rise in the US federal budget deficit as a percentage of GDP, over the next decade, is mostly due to an expected rise in spending relative to GDP, while revenues remain fairly stable (CBO).

That projected spending increase is due to rising health care costs for an aging population, and higher interest rates on federal debt.

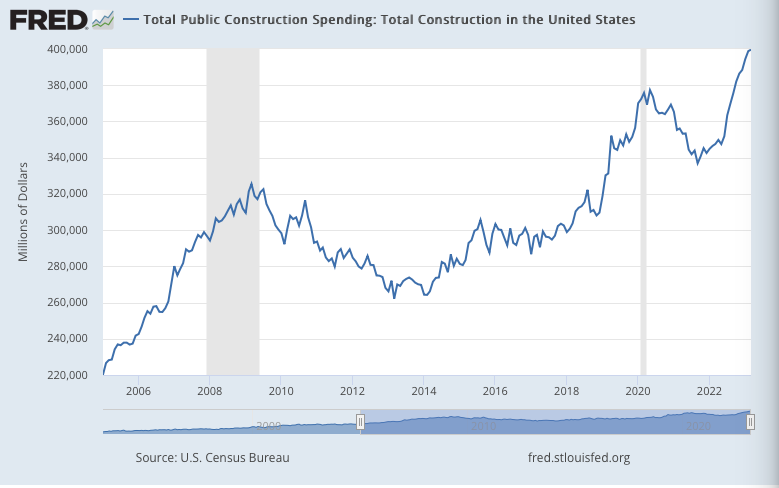
US public construction spending rose +0.2% m/m in March, up +15.0% from a year ago. For Q1 as a whole, spending rose +3.1% q/q, up +14.8% y/y. These numbers are not adjusted to account for inflation, but still indicate a somewhat expansionary fiscal policy.
Leave a Reply